How Does A Polarizing Filter Work
Camera POLARIZING FILTERS
Polarizing filters can increase colour saturation and decrease reflections — and are one of the only lens filters which cannot be replicated using digital photo editing. They are an indispensable tool that should be in every photographer's camera handbag. However, developing an intuition for how a polarizer might impact a photo frequently requires extensive experimentation. This tutorial aims to accelerate that procedure by demonstrating how and why polarizing filters can assistance — and in some cases damage — different types of scenes.
OVERVIEW


In the to a higher place example the polarizer removes the harsh direct glare from the h2o's surface.
Polarizers are placed in front of your camera lens, and work by filtering out sunlight which has been direct reflected toward the camera at specific angles. This is beneficial because the remaining light is often more diffuse and colorful, simply information technology also requires a longer exposure fourth dimension (since light has been discarded). The bending that is filtered is controlled by rotating the polarizer itself, and the strength of this issue can be controlled by irresolute the camera's line of sight relative to the sun.
USING POLARIZERS: SUN ANGLE & FILTER ROTATION
A polarizing filter will be capable of its maximum effect when i's line of sight (in reddish beneath) is perpendicular to the direction of the lord's day:
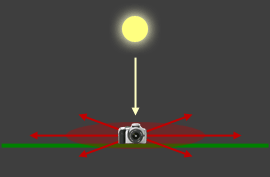
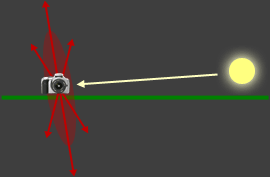
The reddish disks stand for the directions of maximum polarizing capability.
The green lines correspond the footing/horizon.
A good manner to visualize this is to aim your arrow finger at the dominicus while property your pollex direct up. Everywhere your pollex points when you rotate your paw (while still pointing at the lord's day) is where the polarizer is capable of the strongest impact.
Notwithstanding, just because the filter is capable of its maximum effect in the in a higher place directions, this doesn't necessarily mean this is where the image volition appear most effected. Rotating your filter will toggle the bending (relative to the sun) that appears well-nigh polarized. The best fashion to get a feel for this is to rotate the filter while looking through the camera'south viewfinder (or rear LCD), but you lot tin can besides consult the box below for specifics on how this process works.
Notes on Filter Rotation Bending. At one extreme, you can rotate your filter then that the direction of maximum polarization will be perpendicular to the management of the sun (as shown in the above examples). In that instance, the polarizing consequence will be every bit pronounced as possible. If you and then rotate your filter just a piffling (say ten-20°), y'all can shift the bending of maximum effect slightly towards or away from the sun, but in this example the polarizing effect won't be every bit pronounced as before. Equally this angle gets progressively closer to the direction into or away from the sun, the polarizing consequence will appear progressively less pronounced. Finally, once the filter has been rotated a total 90° (to the other extreme), and so no polarizing consequence will be visible. Any more than rotation than this and the polarizing upshot increases once again and the cycle repeats.

Hearst Castle - San Simeon, CA
Since a polarizer'due south result varies with bending, results can appear uneven when using a wide angle lens. Some portions of the scene might be in a direction which is straight into the sunday, whereas others might exist at a right angle to the sun. In that case, one side of the photograph would take a strong polarizer event, whereas the other side would not.
In the example to the left, the sun was most the horizon, so the strip of heaven directly overhead was most influenced past the polarizer (causing it to appear darker), whereas the upper left and lower right regions (nearer the horizon) were much less impacted. If a telephoto lens had been used to photograph only the tower, then the heaven would have appeared much more even.
Although wide angle lenses certainly aren't ideal, rotating the polarizing filter can sometimes brand the result appear more realistic. One approach is to ensure that the most pronounced polarization coincides with the image's edge or corner. This mode the change in polarization will look more similar a natural gradient across the heaven (such as how the sky might appear during twilight).
COLOR SATURATION
One of the offset characteristics that you lot're probable to observe with polarizers is how they increment color saturation:


Columbia River Gorge State Park - Oregon, USA
When direct reflections are reduced, a greater fraction of the subject's light is of the diffuse variety — resulting in a more than colorful representation. Foliage will be rendered with a brighter green, skies volition have a deeper blue and flowers volition appear more intense.
| Select: | No Polarizer | Polarizer at Max |
 | ||
However, saturation isn't e'er increased uniformly. This all depends on whether a detail object is at an optimal bending to the sun, and whether this object is highly reflective. In general, more reflective objects volition run across a greater increment in saturation when using a polarizer. Clear sunny days are also much more heavily influenced by polarizers than overcast or rainy days.
In the case to the right, the result on the stone and leaf is subtle, just the heaven becomes a noticeably darker blue. Accept care non to overdo this effect; unusually night mid-twenty-four hours skies or overly vibrant foliage can easily make photos appear unrealistic.
REFLECTIONS, WINDOWS & TRANSPARENCY
A polarizing filter can be an extremely powerful tool for removing reflections and isolating objects which are moisture, underwater or behind a window. In the case beneath, a polarizer enables the photographer to select betwixt subjects which are reflected from or are underneath the water'south surface:


above examples are courtesy of rickleemorlang
In the above instance, note how the polarizer was unable to remove reflections entirely (although information technology did a pretty good job). This isn't ever possible, but fortunately polarizers are usually able to make reflections imperceptible unless they're relatively intense. Unfortunately the ane exception is with metal surfaces — which oftentimes also happens to be the brightest and least desirable type of reflection.

A polarizer can likewise remove unwanted reflections when taking a photograph out of a window or other transparent barrier. Move your mouse over the example to the left to see how a polarizer eliminates the window reflections. This can be a very useful tool when photographing objects within store windows, out a moving train or within a drinking glass case, for instance.
However, polarizers can also sometimes create an unrealistic-looking rainbow or ripple effect on windows which are uneven, have been tinted or are treated with coatings. A good example of this is something chosen "birefringement," which appears when taking a polarized photo through an airplane window:

above birefringement case courtesy of eaghra (but in a modified form)
Dissimilarity & GLARE
Since polarizers reduce directly reflections, this frequently has the issue of also reducing image contrast. This can make information technology easier to capture scenes with a broad dynamic range, such as trying to residual a brilliant sky with relatively unreflective land (which can even make using a graduated neutral density filter or high dynamic range less of import).
However, less glare/contrast is sometimes undesirable. In the case beneath, the artistic intent was to (literally) highlight the curving road by portraying it in stark contrast to its surroundings. Using a polarizer actually detracted from this goal:


entrance to Canyonlands Isle in the Heaven National Park - Utah, Usa
On the other hand, in most other situations a decrease in glare is desirable and generally creates a more pleasing photograph. For instance, in the in a higher place example the calorie-free doesn't appear as harsh and reflective on the rocks to the far correct.
In other situations polarizers tin can instead increase contrast. In the next example, the polarizer increased contrast by filtering the light reflecting off of the haze and sea spray. This effect appears nigh pronounced in the hills and the puffy clouds directly overhead:


in a higher place examples are courtesy of mikebaird (but in a modified course)
In full general, using a polarizer on clouds and skies will almost always increase contrast, but if the subject itself is highly relfective and then a polarizer will instead likely decrease cotrast.
DISADVANTAGES
While polarizing filters are conspicuously very useful, their disadvantages are that:
- They can make the exposure crave ii-3 stops (four-8X) more low-cal than normal.
- They are one of the most expensive types of filters.
- They require the camera to be pointed at a right angle to the sun for maximal consequence.
- They can accept longer to compose with since they need to be rotated.
- They tin can be difficult to visualize when using the camera's viewfinder.
- They tin potentially reduce image quality if the filter isn't kept perfectly make clean.
- They cannot ordinarily be used with stitched panoramic photos or wide angle shots.

The above panorama would have appeared uneven with a polarizer, and the rainbow could have fifty-fifty disappeared at some positions. Photo from Arches National Park - Utah, Us.
Furthermore, sometimes reflections are essential to a photograph. Two cardinal examples include sunsets and rainbows*; use a polarizer on either and the colorful, reflected low-cal may disappear if the polarizer is rotated for maximum effect.
*Note: polarizers can sometimes enhance the color and contrast of a rainbow past darkening background clouds, but simply if the filter has been rotated just right. Furthermore, including both ends of a rainbow usually requires a wide bending lens, in which case the scene/rainbow may appear uneven.
OTHER TIPS & Farther READING
- Substitute Neutral Density Filter. A polarizing filter can sometimes be used when a longer exposure is needed. This tin can enable an exposure time which is 2-3 stops (four-8X) longer than otherwise possible, which is frequently sufficient for shots of water/waterfalls.
- Pre-Visualize Using Polarized Sunglasses. Wearing untinted polarized sunglasses can exist a helpful manner to pre-visualize how your scene will be captured in a photograph. But exist sure to take these off though when looking through the camera's viewfinder, since the combined effect can forbid you lot from being able to see the prototype.
- Thin Filters on Wide Angle Lenses. A polarizer tin can sometimes create visible darkening in the corners of the epitome ("vignetting") when used on a wide bending lens. To avoid this, yous'll likely need to opt for the more expensive "sparse" variety.
- Circular vs. Linear Polarizers. The circular polarizing variety is designed so that the camera'south metering and autofocus systems can still function. Linear polarizers are much less expensive, but cannot exist used with most digital SLR cameras (since these use through-the-lens (TTL) metering and phase detection autofocus).
For further reading on this topic, besides come across:
- Understanding and Choosing a Camera Lens Filter: Polarizers, UV, ND & GND.
This is a broad overview of all the different filter options available to photographers.


How Does A Polarizing Filter Work,
Source: https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/polarizing-filters.htm
Posted by: brittpreal1963.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Does A Polarizing Filter Work"
Post a Comment